MPLS vs. SD-WAN
There’s no getting around the fact that a reliable and efficient Wide Area Network (WAN) is critical for businesses aiming to streamline operations and enhance connectivity across multiple sites. The goals for any WAN implementation are clear: it should seamlessly interconnect sites, be economical and secure, provide optimal routing, resilience, ensure performance and quality, and, most importantly, be easy to manage. Two prominent solutions, MPLS with legacy routers and SD-WAN, have emerged to meet these objectives, each with its unique advantages and considerations.

MPLS with Legacy Routers: A Legacy Approach with Proven Effectiveness
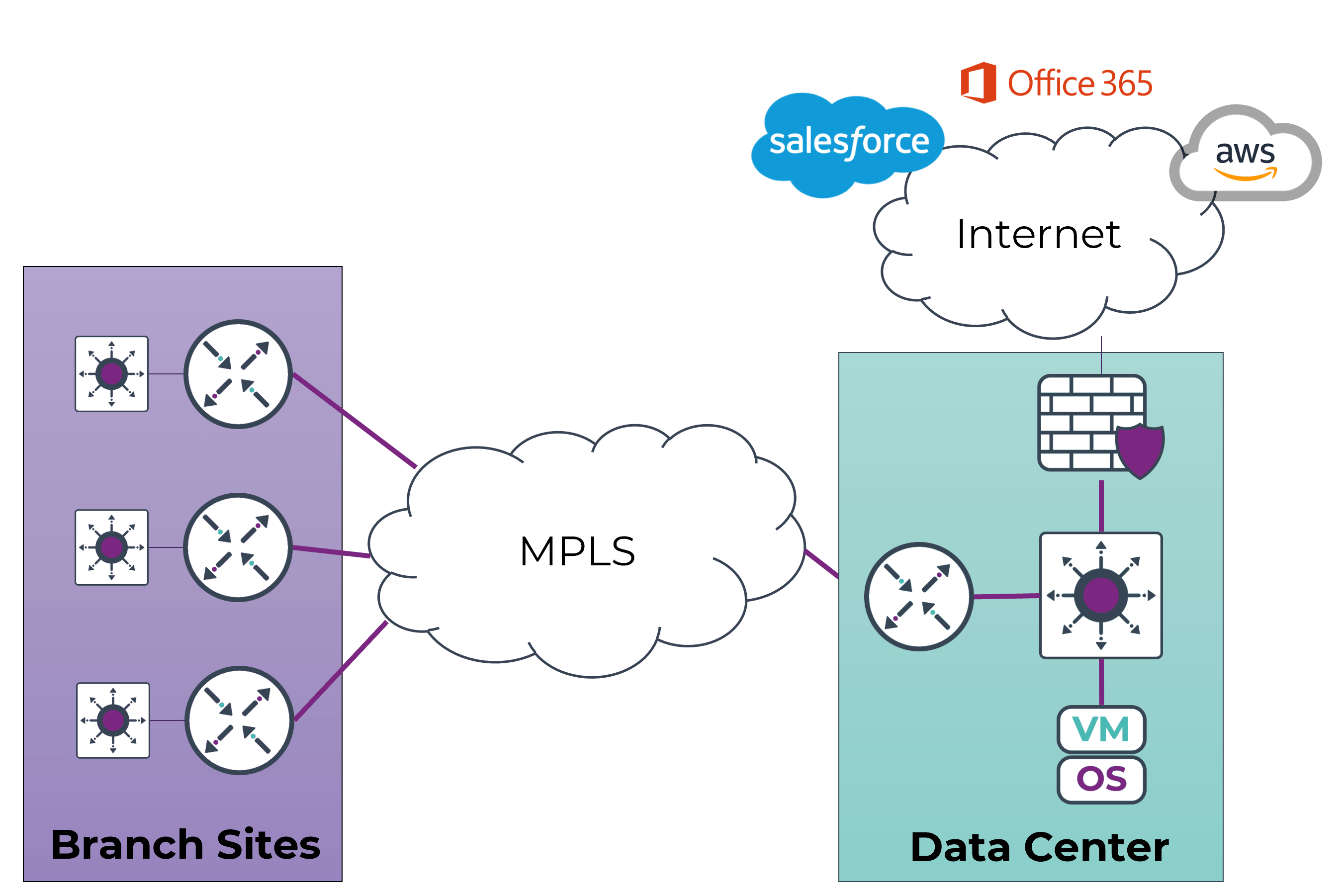
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) with legacy routers has long been a stalwart in the networking domain, offering Layer 2 or Layer 3 VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) from service providers.
The appeal lies in its any-to-any connectivity, dedicated bandwidth, and the assurance of Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for Quality of Service (QoS). Particularly suitable for mission-critical applications and voice/video data, MPLS with legacy routers relies on traditional routing protocols, providing predictable performance, reliability, and availability.
However, MPLS isn’t without its challenges, and understanding these limitations is important in making an informed decision about WAN infrastructure.
- Limited Availability and Bandwidth Constraints: One significant challenge with MPLS lies in its uneven availability across geographical areas. In regions where MPLS infrastructure is not readily accessible, organizations may face connectivity issues and struggle to establish a consistent network framework. Additionally, MPLS services often come with bandwidth limitations, restricting the volume of data that can be transmitted. As businesses expand, these limitations can become a hindrance to seamless operations.
- Diverse Time-to-Repair Based on Location: The time it takes to repair MPLS connections can vary significantly based on location. Remote or less accessible areas may experience prolonged downtime during repairs, impacting overall network reliability and business continuity.
- Individual Management of CE Routers: Managing Customer Edge (CE) routers individually can be a cumbersome task for network administrators. The decentralized nature of this approach increases the complexity of network management, making it challenging to implement uniform changes across the entire network.
- Trust in ISP Private Network or Increased Cost for Security: MPLS inherently relies on the trust of Service Providers (SPs) to secure the private network. While this may suffice for some organizations, security-conscious enterprises may find it necessary to enhance protection at each branch location, thereby increasing costs and introducing additional management overhead. Opting for increased security measures, such as deploying Firewalls (FW) or encryption at each branch, adds a layer of complexity to the management process and elevates the overall cost of the MPLS setup.
So, while MPLS provides a networking solution with proven reliability, there are challenges that necessitate careful evaluation of these limitations.
SD-WAN: Transforming Network Architecture with Intelligence
As organizations continue to navigate the complexities of modern networking, Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) has emerged as a transformative solution, offering a dynamic and agile approach to connectivity that’s made SD-WAN a game-changer in the realm of networking.
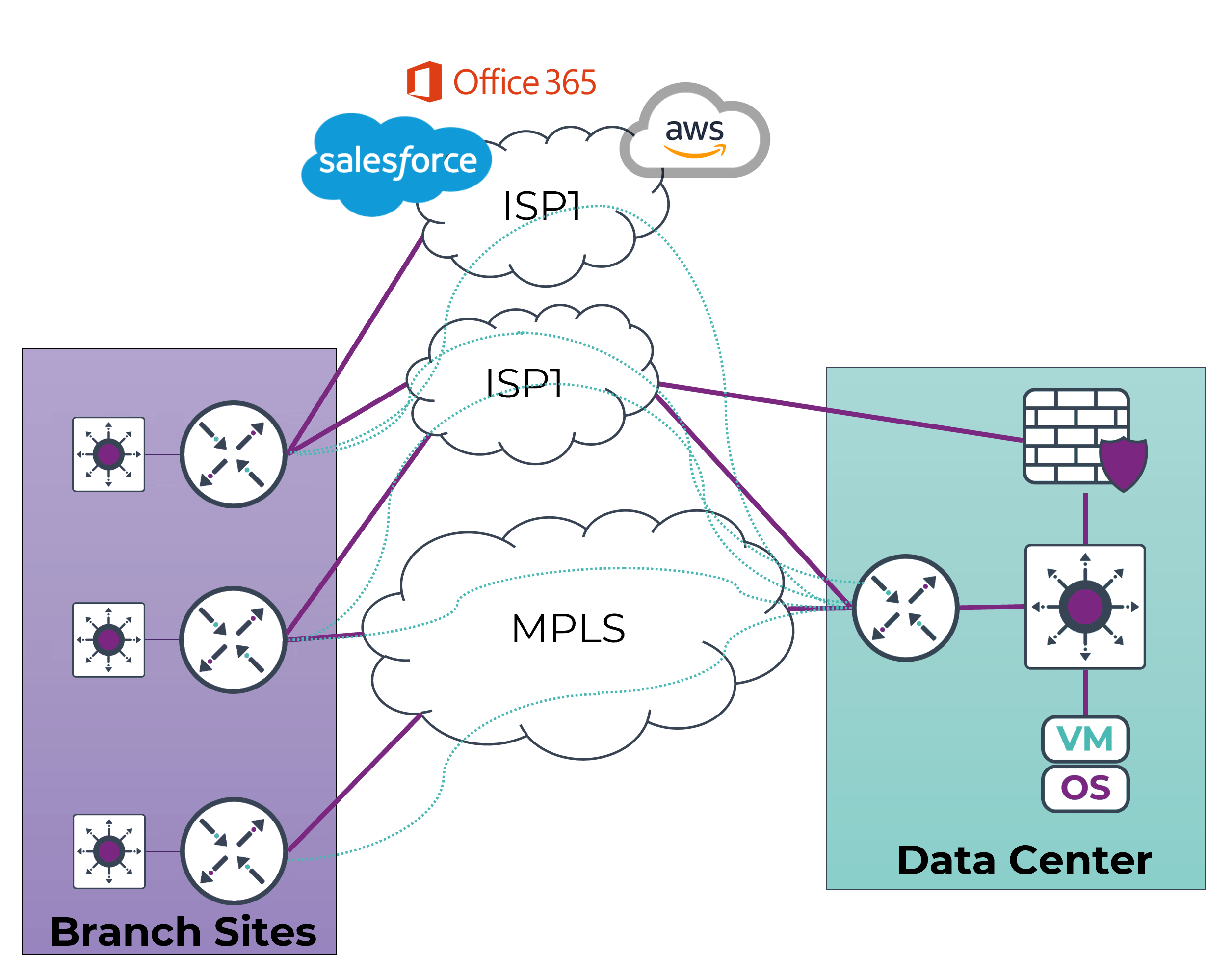
- Utilization of Tunneling Technology for Overlay: SD-WAN leverages tunneling technology to create an overlay network, allowing organizations to establish secure connections over existing infrastructure. This overlay architecture provides flexibility and adaptability, enabling seamless integration with various transport options.
- Transport Independence: One of the defining characteristics of SD-WAN is its transport independence. This means that it can operate over a variety of network connections, including MPLS, broadband internet, and LTE. This flexibility ensures that organizations can choose the most cost-effective and reliable transport options based on their specific requirements.
- Application-Aware Routing: SD-WAN introduces a level of intelligence into routing decisions by being application-aware. This enables the network to prioritize and optimize traffic based on the specific requirements of each application, ensuring optimal performance and responsiveness.
- Path Conditioning for Enhanced Reliability: SD-WAN includes path conditioning capabilities, allowing it to dynamically adapt to changes in network conditions. This ensures a more reliable and resilient network, as the system can intelligently route traffic along the most stable paths available.
- Centralized Management: Centralized management is a cornerstone of SD-WAN, providing a unified control point for network administrators. This centralized approach streamlines network management, making it more efficient and responsive to the evolving needs of the organization.
- Security at the Forefront: SD-WAN prioritizes security by offering direct access to SaaS (Software as a Service) applications and the internet. This direct access, coupled with advanced security features, enhances overall network security and reduces the reliance on trusting ISPs with private networks.
- Carrier Independency and Traffic Shaping: SD-WAN liberates organizations from dependence on a single carrier, allowing them to choose the most suitable carrier for each location. This independence, combined with traffic shaping capabilities, empowers businesses to optimize their network performance according to their specific needs.
- Cost Efficiency and Consolidated Functions: Embracing commodity internet for connectivity lowers costs significantly, while simultaneously increasing reliability and availability. SD-WAN also consolidates various networking functions, reducing the complexity and cost associated with maintaining multiple appliances.
- Flexible Application Security: SD-WAN offers the flexibility to secure applications at the branch, data center, or cloud. This adaptability aligns with the diverse deployment scenarios of modern businesses, providing a tailored approach to application security.
- Traffic Shaping for Business Needs: SD-WAN allows for granular traffic shaping, enabling organizations to prioritize and shape network traffic based on the unique requirements of their business. This ensures that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and performance.
Why is SD-WAN so Efficient?
SD-WAN stands out as an exceptionally efficient solution for WAN due to three key attributes. Firstly, its intelligent routing capabilities enable the system to dynamically adapt to real-time network conditions, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. This adaptability is crucial in network traffic that’s constantly changing.
Moreover, the centralized management console of SD-WAN plays a pivotal role in simplifying network administration. This centralized approach enhances intuitiveness and responsiveness, making it easier for organizations to manage and deploy network resources efficiently.
Lastly, SD-WAN brings about substantial cost efficiencies by leveraging multiple transport options, including cost-effective broadband internet, thereby reducing dependence on expensive dedicated lines. This point is extremely important, as WAN architectures leveraging internet-based transports are becoming prevalent as applications shift from on-premises data centers to SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS offerings. Secure architectures leveraging Direct Internet Access (DIA) capabilities are efficient for XaaS connectivity as they eliminate the ususal latency required to first pass through a data center, and reach cloud applications directly.
The inherent flexibility of SD-WAN allows businesses to promptly adjust to changing bandwidth requirements, making it a highly adaptable and cost-effective solution in the dynamics of modern networking.
Focus on Security
As enterprises move towards SD-WAN architectures that leverage internet access as a transport, there is a desire to leverage these circuits to reach cloud applications directly from the branch. It is critical to do this in a secure fashion that does not leave users and data at risk. SD-WAN architectures solve this problem in a few typical ways.
The first approach is to backhaul traffic through an on-premise hub data center with a security stack. Internet-bound traffic would be first sent to this location, inspected by the security stack in this facility, and then use the data center’s internet connection to reach the application in the cloud. This is a similar architecture to many MPLS deployments. It is inefficient as it adds latency, but does leverage existing investments.
The second approach is to leverage on-box features of SD-WAN platforms to provide security for users and systems. Many solutions offer native security features such as Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) inspection, URL filtering, and DNS security in order to provide a base level of security. Traffic destined for cloud applications is sent out directly from the branch to the internet, and security services are delivered locally.
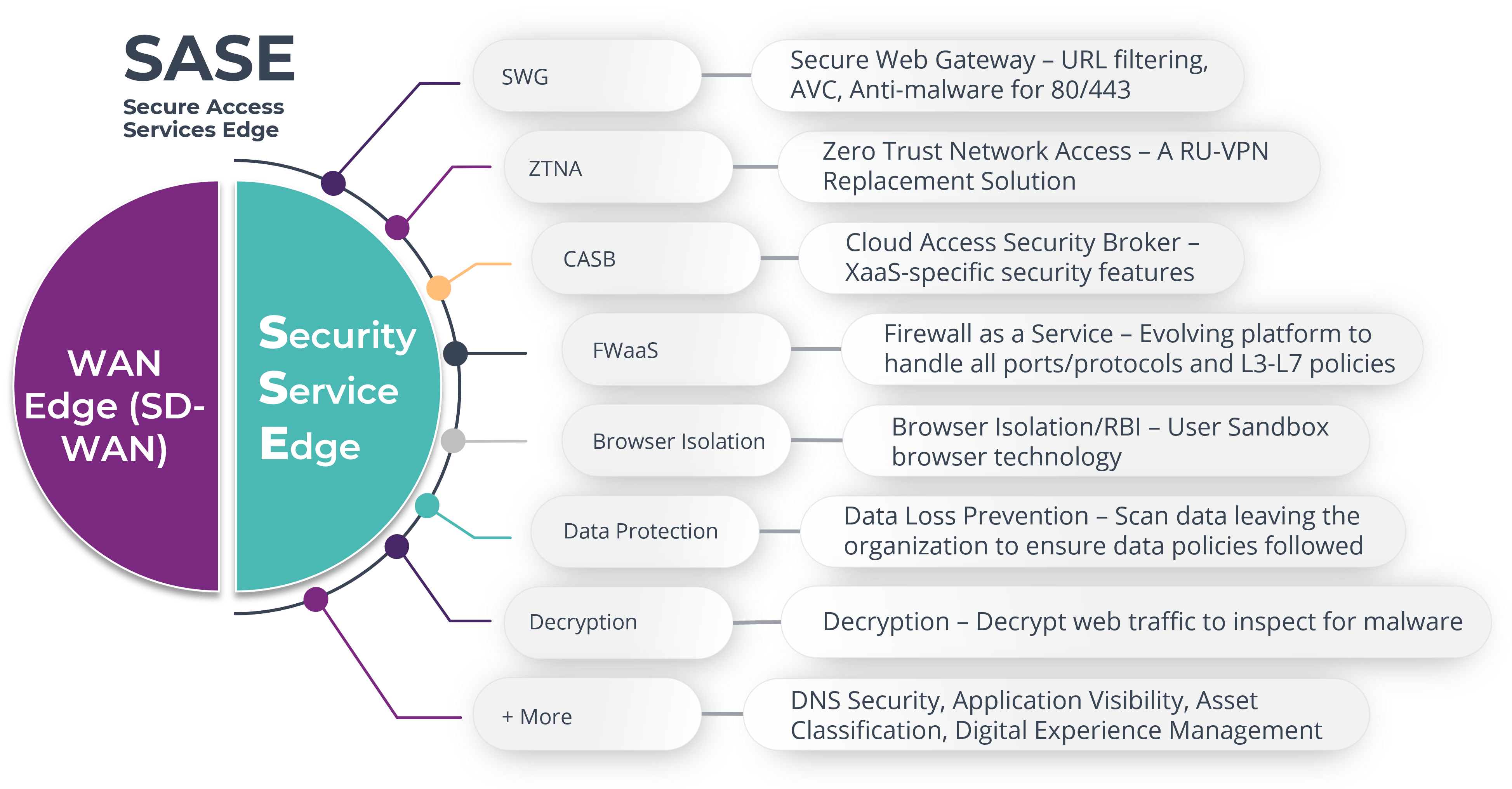
The final, and most promising approach, is to leverage Security Services Edge (SSE) solutions to tunnel traffic to the nearest security Point of Presence (POP) in order for traffic to be decrypted, inspected, and secured before it makes its way to the application. SSE is a suite of cloud-delivered secuirty features that are delivered as a Service. There is a trend of OEMs such as Cisco, Systems Palo Alto Networks, and HPE Aruba Networks to offer a combined SD-WAN plus SSE solution, that has been dubbed Secure Access Services Edge (SASE) by Gartner. However, it is possible to take a best of breed approach and select a SD-WAN and SSE solution from two different vendors, and conduct an integration via APIs and open-standard approaches.
Application Direct Internet Access (DIA) enabled by SD-WAN architectures offer immense promise through business benefits, but must be approached with security at the top of mind.
Build Your Long-term WAN with SD-WAN
As businesses strive to meet today’s high-performance demands, the choice between MPLS with legacy routers and SD-WAN becomes an easy one. While MPLS offers proven reliability, SD-WAN presents a forward-looking, agile solution that aligns with the active nature of modern business environments. As organizations evaluate their WAN needs, understanding the strengths and trade-offs of each approach is key to making an informed decision that aligns with their overarching business goals.

Matt Martinez
Director – Secure Integrated Architectures (SIA) | CCIE R&S #42200
Matt Martinez is an IT and Cybersecurity professional who has 15 years of experience designing, deploying, troubleshooting, and optimizing critical systems. His background is heavy in consulting, with emphasis in large scale, multi-discipline projects such as infrastructure transformation, data center consolidation/migration, and security architecture. He has holistic expertise in network, security, and data center infrastructure technologies. Software-Defined Network technologies such as SD-WAN and Cisco’s Application Centric Infrastructure are some of his specialties, as well as security technologies such as Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW) and Security Services Edge (SSE) from multiple OEMs.
At ANM he is the Director of the Secure Integrated Architectures team, where he and his team focus on multi-discipline client architectures as well a strategic initiatives such as developing ANM’s Zero Trust Architecture workshops. He also is Director of the Network Practice, where he helps define and refine ANM’s portfolio in this solution space, where he is constantly vetting and putting technologies to the test, especially newer products. Matt is also the lead architect for ANM Technology Labs, which are used for demonstrations, proof of concepts, and training.
Network Security Predictions for 2025
As organizations continue to evolve in world filled with bad actors, network security remains a cornerstone of their operational integrity. With 2025 now here, emerging technologies and evolving threats are set to redefine the cybersecurity landscape. Here, we explore...
Keep Your Data Secure this Holiday Season
As the holiday season is upon us, our lives become a flurry of activity: gift shopping, traveling, and catching up with loved ones. While the festivities are a joy, the increased online activity during this time creates a fertile ground for cybercriminals. Staying...
Embracing Gratitude: How Technology Enriches Our Lives Every Day
As Thanksgiving approaches, we’re reminded to pause and appreciate the many aspects of life that enhance our well-being. Often, family, health, and prosperity come to mind. However, there’s one element we might overlook as we gather for the holiday season: the...


